Published on October 31, 2018 by Nachiketa Trivedi
Statoil, a Norwegian oil and gas firm, has to continue to rationalize its carbon footprint and drive diversification toward renewable energy production, to align with investor and shareholder interest and reduce susceptibility to climate and regulatory change. Elsewhere, a global investment major is in talks with Japan Tobacco Inc. to put in place mechanisms to fight child labor in its tobacco supply chain. Such instances are not isolated. Across the globe, a consortium of investment management firms, led by the world’s largest independent asset manager, BlackRock, has engaged with 32 US-listed firms to urge them to collaborate with the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) to develop cost-effective and relevant environmental, social and governance (ESG) reporting standards for various industries.
The common thread here is an emerging investment theme that has the potential to change the way money is managed. While there is some fluidity in the terminology, we choose to call this investment methodology based on ESG concerns “responsible investing” (RI). This is a broad term meant to include more specific investment approaches such as “ethical investing” and “ESG integration”.

Studies indicate that RI helps to manage risk better and produces sustainable long-term returns. Authors of a research report published in the Journal of Applied Corporate Finance talk of “an unequivocally positive contribution to risk-adjusted returns when using a 10% best-in-class ESG screening approach (one that effectively removes companies with the lowest 10% of ESG rankings), both in a global and a developed-market universe”1 .
The study, including others, points to a positive correlation between RI and performance2 . As we move away from a traditional exclusionary approach to a more integrated RI approach, we expect performance to only get better3 . Indeed, investors, particularly big-ticket ones with longer investment horizons, have sat up and taken notice. Eighty percent of 475 of the largest global investment institutions recently surveyed4 by State Street Global Advisors say that ESG standards are part of their investment plans. Seventy-five percent of these investors expect the same performance from these strategies as they would from traditional ones. Notably, ESG performance did not disappoint; 68% of the institutions reported improved performance, and 69% could better control portfolio volatility.
As institutional investors express more interest, asset managers have started to formulate new strategies that integrate RI and to re-position existing strategies to include RI parameters. RI has evolved from the early days of negative screens to a more seamless integration of ESG considerations.
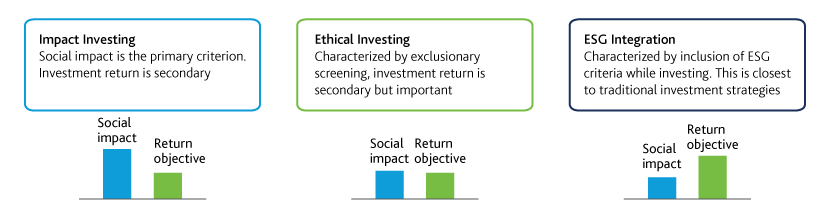
Responsible Investment Strategy Categorization5 : Although definitions and categorizations vary based on nuances and distinctions, RI can be broadly divided into the following investment methodologies:
-
Impact Investing: A form of socially conscious investing, this is, in essence, not far removed from pure philanthropy, with the return objective secondary to social impact.
-
Ethical Investing (EI): Next on the scale, EI entails the exclusion of certain stocks, based on investor discretion. These include nuclear weapons, tobacco and alcohol. While social impact is intended, EI balances social impact with return objective.
-
ESG Integration: This is the closest to traditional investment strategies, with a clear performance objective. Methods of integrating ESG standards into investment strategies include incorporating ESG criteria when screening stocks and considering ESG factors during due diligence.
Adoption of these approaches shows distinct regional patterns: exclusionary screening is popular in Europe, and ESG integration finds wider acceptance in the US, Canada, Australia/New Zealand and Asia ex-Japan. In Japan, investors tend to practice RI through shareholder action and corporate engagement, both of which could be classified as modes of ESG integration.6
Impact of ESG on Investment Communications: As ESG concerns become mainstream, they are gradually becoming critical in the assessment and selection of institutional investors. Some of the world’s top pension funds report inclusion of dedicated ESG questionnaires and annual ESG due diligence as integral to manager selection and assessment in their United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment (UN PRI) filings. ESG concerns are also becoming part of due diligence questionnaires (DDQs) that money managers receive.7,8, At a recently held conference, global asset manager Neuberger Berman (which has USD304bn in assets under management) reported that ESG information is requested in almost 50% of DDQs it receives from European and US clients.9 Widely used investment manager databases have also updated their ESG questionnaires to enable managers to better position their ESG narratives.10
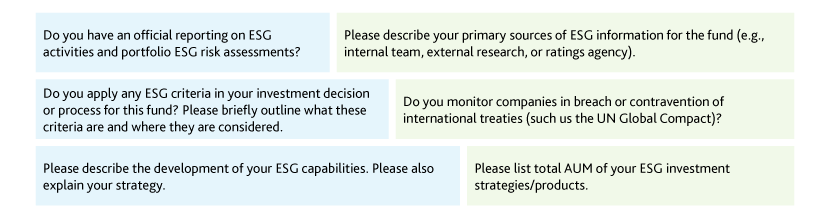
In RFPs and DDQs, investment managers are required to highlight their compliance with ESG frameworks and mode of inclusion of ESG considerations in investment strategies. Client questionnaires look not only at qualitative aspects but also at quantitative aspects, such as consolidated ESG assets under management, UN PRI assessment scores, and human capital dedicated to ESG issues. The following are some client questions.
Subject-matter experts and RFP specialists face a steep learning curve in terms of how best to communicate their ESG expertise. Achieving proficiency in reporting and communication demands more from the various teams involved, especially due to the continually changing ESG investing landscape and understanding. Targeted in-house training, dedicated ESG experts and committees, and active participation in industry forums can help asset managers develop the needed ESG expertise. Also, RFP teams need to work with investment teams and ESG specialists to develop uniform and compelling language covering ESG philosophy and process, to be included as part of an RFP library that could be used by teams across the globe.
Challenges in ESG Adoption: Although all the pieces of the puzzle seem to be falling into place, investors cite the lack of clear measures of ESG performance and inadequate reporting as barriers to ESG adoption. Another unique challenge is the cost of ESG integration. ESG investing is based on a long-term perspective, but costs are immediate and have to be borne upfront.
Future of ESG: Those currently at the forefront of ESG adoption are institutional investors who control a considerable part of global equity market capitalization. With strong ESG adoption in Europe, the US catching up, and Asian behemoths Japan and China waking up to the need for ESG-centered investments, we believe ESG is set to become a dominant investing trend.
As ESG standards find wider acceptance, we expect algorithms driving these strategies, and data availability and standardization to improve, ultimately translating into better performance and lower costs, and spurring demand for ESG products. It seems that despite the challenges, the future of ESG is bright.
Acuity Knowledge Partners’ Fund Marketing Services arm offers a range of services to help clients with their marketing and investment communication efforts. We work with prominent investment management firms to respond to RFPs and DDQs, including ESG-focused proposals. We leverage the rich and extensive experience of our RFP specialists, experience they have built over the years by working with leading asset management firms, to help clients position their companies better and compile winning proposals.
Sources
1. https://medium.com/the-esg-advisor/more-evidence-of-solid-esg-performance-a83cb681fde3
2. https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/111816/how-esg-sri-and-impact-funds-differ.asp
What's your view?
About the Author
Nachiketa Trivedi is a senior RFP writer at Acuity Knowledge Partners with over six years of experience in asset management and information technology. Nachiketa, who joined Acuity Knowledge Partners in June 2017, has worked across various asset classes. Prior to joining Acuity Knowledge Partners, he was with Invesco Asset Management where coordinated and completed RFIs/RFPs/DDQs for institutional and retail clients based in Asia (ex-Japan, ex-Australia). Prior to that, Nachiketa worked for Infosys in its banking platform Finacle as an Associate Consultant responsible for presales and business development activities. Nachiketa holds a Masters in Business Administration and a Bachelors in Technology (Civil Engineering).
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox









