Published on April 14, 2021 by Prashant Gupta
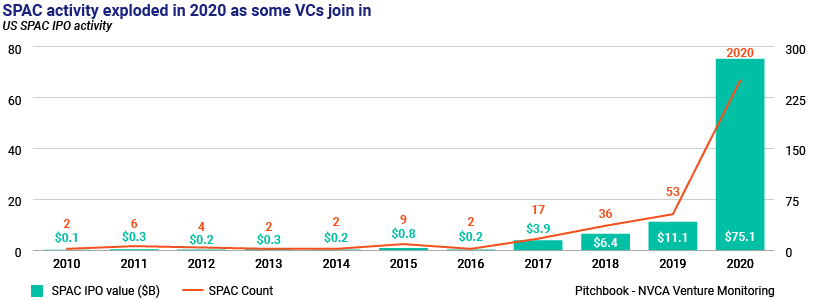
Special-purpose acquisition companies (SPACs) have become a notable trend in the IPO world amid the pandemic. Considered to be an alternative route to taking companies public, SPACs raised more capital in the US in 2020 than over the entire preceding decade.
The number of public listings of SPAC vehicles grew fivefold to 250 in 2020 from 53 in 2019, recording a c.580% jump in the value raised to USD75bn, according to a 4Q 2020 PitchBook – NVCA Venture Monitor report.
Understanding blank-cheque companies: A SPAC is also known as a “blank-cheque” company. It is a public shell company, i.e., it has no operations. It is typically set up by notable investors (known as “sponsor”) with the sole purpose of taking a promising private company (known as a “target”) public by merging with it and generating good returns in the long term.
Of course, a SPAC is also an opportunity to invest in a good management team or a good entrepreneur.
A way of bypassing the traditional IPO: Upon merger of a private entity with a SPAC, the private entity effectively becomes a public company, is listed on an exchange and is assigned a ticker. In other words, a shell SPAC has now been transformed into a fully operational company, and the investors who initially owned shares in the blank-cheque company now own a share of the well-operated public entity.
When a SPAC is formed, the sponsor, and often the management team, contribute a nominal amount for an equity stake (often referred to as “founders’ stock”) in the SPAC, which usually represents c.20% of the stock in the SPAC after its IPO. The founders’ stock is intended to be used to find a potential target and effect a merger. The remaining c.80% interest is subscribed to by others through “units” allocated in the SPAC’s IPO. These units consist of a share of “common stock” and a fraction of a warrant.
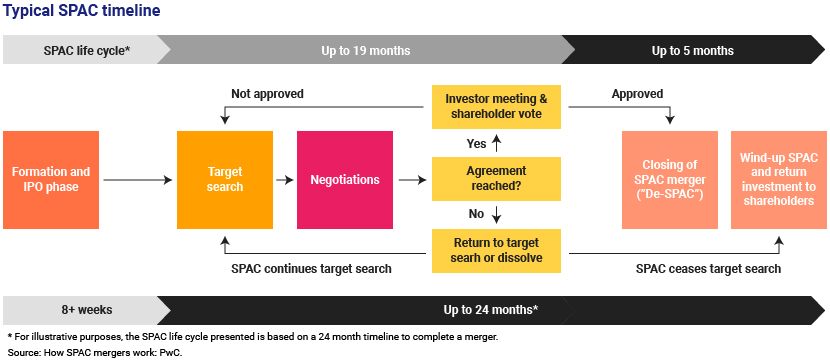
From SPACing to de-SPACing or liquidation? The capital the IPO raises is placed in a trust account, typically interest-bearing, until the SPAC’s management team finds a promising target looking to go public. The SPAC has a timeframe, typically 18-24 months, within which to find a target and merge with it, referred to as de-SPACing. Otherwise, the SPAC is liquidated and the proceeds from the IPO returned to the shareholders unless the timeline is extended via a proxy process.
A look at the lifecycle of a SPAC:
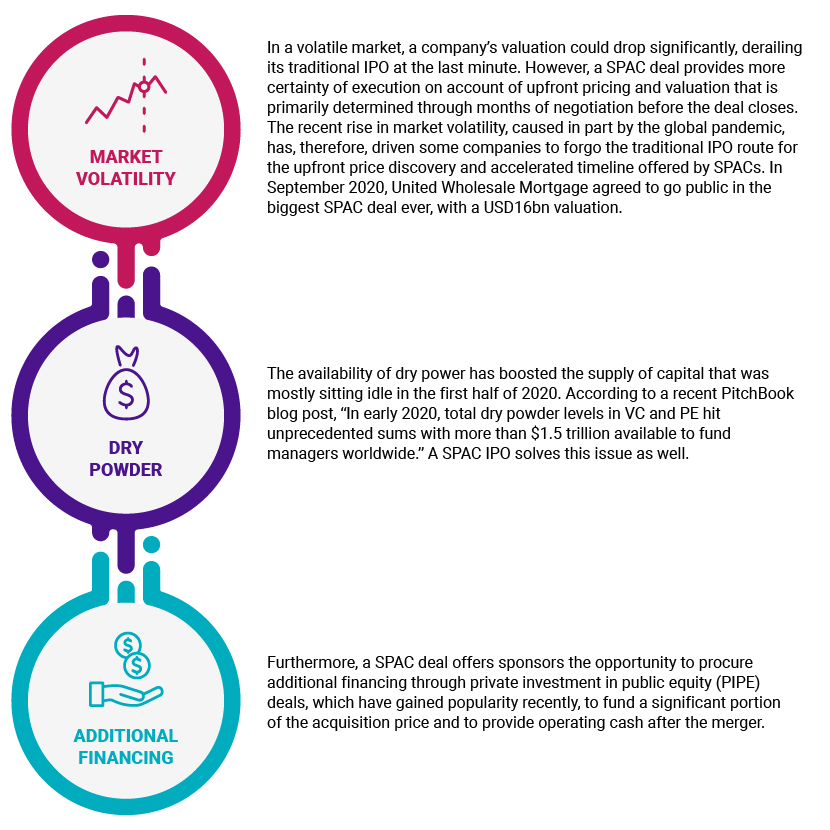
What is driving the increase in SPACs? SPACs have been around for decades (the first SPAC was launched in the 1990s); initially, they were the last resort for small companies that found it challenging to raise capital in the open market, but they have become very popular recently. Increased use of SPAC IPOs is the result of many factors, some of which are listed below.
Way forward: We expect this trend to continue as an increasing number of major PE/VC firms, notable investors and high-profile entrepreneurs form more SPACs and continue to attract companies looking to go public. However, there are several challenges:

Investors with the appropriate experience and skillset may be able to identify such companies, but it requires significant effort and resources. This puts pressure on the investment team, as it leaves limited room for deal execution.
Acuity Knowledge Partners can ease some of this pressure by sharing the workload. We have a team of professionals with experience in advising companies throughout the lifecycle of the SPAC process. Our PE/VC experts provide cost-effective one-stop solutions to market participants and help them stay abreast of the latest market trends, find good deals, conduct deeper diligence, carry out more meaningful valuation studies, set up effective monitoring processes and access strategic research experts to work closely with companies.
Sources:
PitchBook – NVCA Venture Monitor: US VC ecosystem
SEC.gov | What You Need to Know About SPACs – Investor Bulletin
A Primer on SPACs – Risks and Trends | Deloitte US
Tags:
What's your view?
About the Author
Prashant is a seasoned professional within the Private Market team and has been with the company for over 12 years. His extensive career spans more than 18 years, during which he has garnered a wealth of experience through a diverse range of research and analysis assignments. His clientele is impressive and varied, including top-tier asset managers, private equity firms, and bulge bracket investment banks.
His expertise is broad and deep, with a particular focus on comprehensive end-to-end credit analysis.Prashant’s skill set encompasses capital structure analysis, intricate corporate structure assessments—including guarantees and structural subordination cases—and covenant compliance analysis. Additionally, he is adept at financial modeling and valuation, asset recovery analysis,..Show More
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox