Published on September 17, 2025 by Shreya and Vandana
Introduction
The crisis relating to Red Sea trade routes has been causing severe disruption to global supply chains since 3Q 2023, driven primarily by the ongoing geopolitical tensions and the attacks by Houthi rebels based in Yemen targeting commercial vessels. The Red Sea is a crucial sea link between Europe and Asia via the Suez Canal, one of the world's most critical maritime corridors, impacting trade volume, shipping costs and efficiency of global logistics.
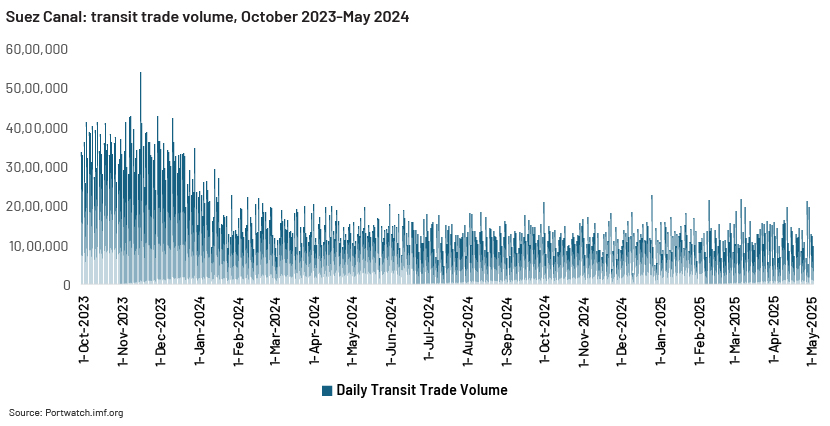
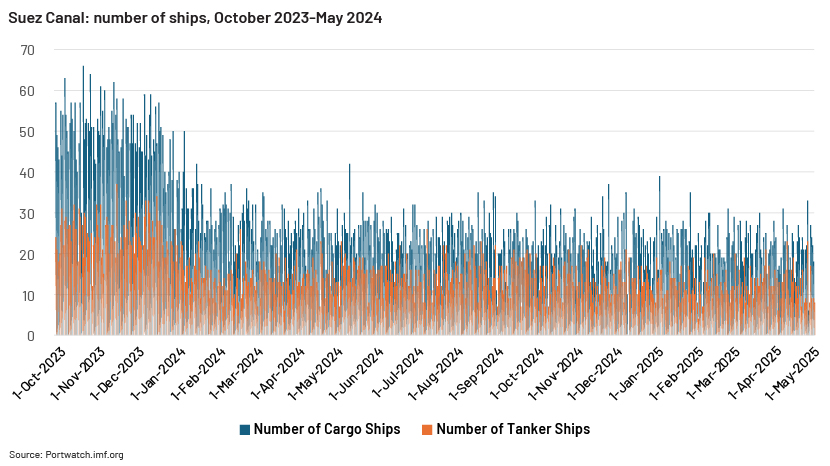
The Red Sea’s strategic importance for global trade
The Red Sea plays a significant role in global trade and energy security due to its strategic location, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Indian Ocean. This strait serves as a shortcut for maritime traffic between Asia and Europe, handling a large part of global container movement.
It provides access to the Suez Canal, through which approximately 12% of global trade and 30% of container traffic flow, making Suez Canal disruptions a critical risk factor for global shipping and logistics. Countries such as India depend on this route, with nearly 80% of its exports passing through the Red Sea. Additionally, around 40% of trade between Asia and Europe depends on this passage. The recent crisis in the region has disrupted supply chains worldwide, leading to a sharp decline in exports from major economies such as the European Union and Germany, two of the largest global exporters.
Timeline of the crisis
The dispute between the Houthi rebels in Yemen and the US escalated sharply on 8 November 2023, with the Houthis attacking a US drone. This led to further confrontations in the region.
On 19 November, the situation worsened with the Houthis launching attacks on commercial shipping vessels in the Red Sea. Claiming solidarity with Gaza, they targeted ships they believed were linked to Israel. During these attacks, missiles were fired at three commercial vessels. They seized a cargo ship named Galaxy Leader and held 25 hostages.
The conflict continued until December 2023, when the Houthis fired a missile at commercial tanker M/T Strinda in the Bab el-Mandab Strait, a critical maritime chokepoint. These actions hampered international shipping operations and regional stability.
The US and the UK, with support from Canada, Bahrain and Australia, made coordinated efforts, with military strikes on 60 Houthi targets. This operation, named “Poseidon Archer”, aimed to restore security and peace in the Red Sea.
Houthi forces used Houthi unmanned surface vessels (USVs) in the Red Sea in 2024. They also launched a missile towards the Israeli city of Eilat, which was successfully intercepted by Israeli defence systems. These developments highlight the ongoing volatility in the region and the broader implications for global maritime security and trade.

Impact on shipping and costs
The continued crisis in the Red Sea is a major concern, with the impact of the Red Sea crisis on global trade evident in disrupted maritime routes and widespread supply-chain challenges. Strategic chokepoints such as the Bab el-Mandab Strait and the Suez Canal have witnessed a sharp decline in traffic, reflecting the severity of the situation.
Companies are facing logistical hurdles due to instability in the region, with the Red Sea crisis impact on shipping leading to rerouting, higher costs, and unpredictable delivery timelines. Shipments are following alternate, longer routes, leading to higher shipping and operating costs, further highlighting the Red Sea crisis impact on supply chain reliability and efficiency. This results in unscheduled deliveries, extended transit times and complicated supply-chain planning and execution.
The crisis has inflated insurance premiums and freight container rates, further straining global trade operations. Maritime transport has become more expensive and unpredictable, impacting both exporters and importers across the globe.

The Red Sea crisis has become a global concern affecting international trade and economic stability, with the Red Sea crisis impact on supply chain efficiency being felt across multiple economies. Vessel traffic has declined sharply, contributing to disruptions in supply chains, oil-spill risks and rising inflationary pressures across multiple economies. These challenges have led to an increase in the Global Supply Chain Stress Index, which surged to 2.3m TEUs in December 2024, reflecting the widespread impact on shipping volumes and logistics.
The Red Sea crisis has exposed the need for more resilient and diversified global supply chains. Companies are rethinking their reliance on specific routes and suppliers to reduce disruption risks. Key strategies such as data-driven risk management, strategic sourcing and tech-enabled transparency are being adopted for better visibility and collaboration. Companies with domestic sourcing are less affected. As it is a major transit hub, disruptions in the Red Sea have led to rising costs, especially as retailers and manufacturers in Western Europe and North America struggle to access essential goods.
Port congestion has worsened due to shifting service patterns and rising cargo volumes, with Red Sea-related diversions adding pressure. Fewer but longer mainline calls, larger parcel sizes and increased dwell times, especially at Jebel Ali, are straining inland logistics. Seasonal events and weather disruptions have further impacted operations. Ports across Southeast Asia and the Middle East, including Singapore and Dubai, are facing delays. Despite these challenges, efforts to maintain efficiency and reduce disruption continue.
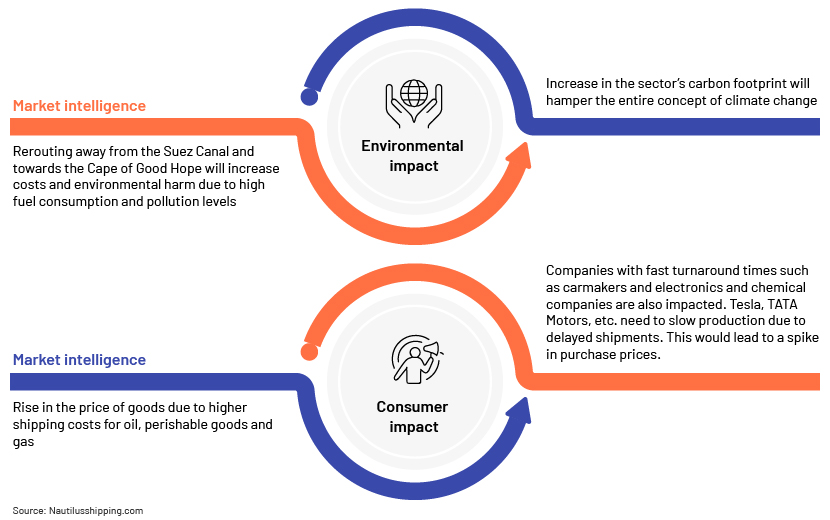
Environmental and consumer impact
The rerouting of maritime traffic away from the Suez Canal towards the longer path via the Cape of Good Hope has major environmental and economic consequences. This has led to increased fuel consumption and carbon emissions due to extended durations, intensifying environmental degradation. Longer transit times have also disrupted delivery schedules and raised transport costs, ultimately affecting end consumers through higher prices and reduced availability of goods.
Impact of Red Sea crisis by sector
The Houthi attack on cargo ships in retaliation to Israel’s offensives against Hamas in Gaza has caused a major rerouting of goods traffic away from the Suez Canal towards the tip of Africa. This has caused significant delays in deliveries and increased shipping costs and geopolitical tensions across the globe. The impact of the Red Sea crisis by sector is illustrated below.
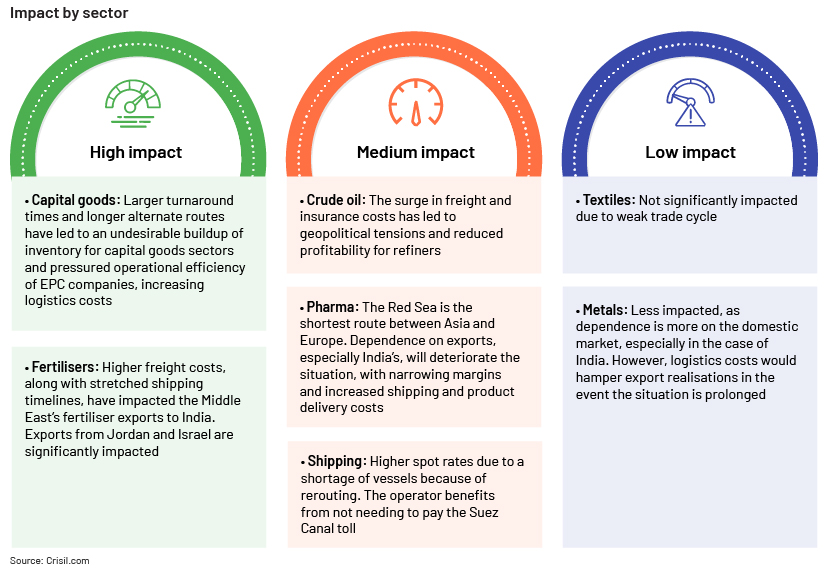
-
Textiles: Not significantly impacted due to weak trade cycle
-
Metals: Less impacted, as dependence is more on the domestic market, especially in the case of However, logistics costs would hamper export realisations in the event the situation is prolonged
-
Shipping: Higher spot rates due to a shortage of vessels because of rerouting. The operator benefits from not needing to pay the Suez Canal toll
-
Capital goods: Larger turnaround times and longer alternate routes have led to an undesirable buildup of inventory for capital goods sectors and pressured operational efficiency of EPC companies, increasing logistics costs
-
Fertilisers: Higher freight costs, along with stretched shipping timelines, have impacted the Middle East’s fertiliser exports to India. Exports from Jordan and Israel are significantly impacted
-
Crude oil: The surge in freight and insurance costs has led to geopolitical tensions and reduced profitability for refiners
Impact by sector
-
Pharma: The Red Sea is the shortest route between Asia and Europe. Dependence on exports, especially India’s, will deteriorate the situation, with narrowing margins and increased shipping and product delivery costs
Outlook
Initiatives such the US-led “Operation Prosperity Guardian” mission have been implemented at a global level to combat the impact of the Red Sea crisis. These aim to restore and safeguard maritime operations. Companies are also exploring alternate routes and working together towards better practices to reduce costs. A unified approach is being followed by the US, together with countries such as the UK, Canada, France and Bahrain.
Corporations worldwide are actively exploring alternate shipping routes and adopting collaborative strategies to mitigate rising costs and operational disruptions. Technology plays a critical role in enhancing security, monitoring vessel movements and predicting potential threats. Real-time tracking and data analytics are helping organisations anticipate adverse conditions and respond proactively.
Conclusion
The Red Sea is as a critical maritime corridor linking Asia with Europe and North America. The crisis in the region is a significant disruption, demanding a unified international response. Businesses across the globe are working to mitigate increased shipping and operating costs, prolonged transit times and greater risks of future attacks.
To strengthen resilience against such disruptions, it is essential for both nations and corporations to take proactive measures, especially given the ongoing Red Sea crisis impact on supply chain networks and trade flows. Forming strategic alliances, sharing resources and fostering international cooperation could help reduce the impact of future crises. Embracing advanced technologies and upgrading existing infrastructure are also key to minimising supply-chain vulnerabilities. Real-time monitoring systems, predictive analytics and diversified logistics strategies can enable organisations to respond swiftly and effectively to emerging threats, ensuring continuity and cost-efficiency in global trade operations.
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can help
Acuity Knowledge Partners provide customised research and analytical solutions that assist clients understand the effects of geopolitical crises on sectors and economies. With extensive knowledge of tracking and analysing global trends, we create newsletters, dashboards and industry reports and provide on-demand analyses. Our comprehensive range of services enable clients to foresee market changes and geopolitical threats. We also help clients discover new opportunities relating to infrastructure, such as alternative land and sea routes and relevant ports, logistics centres and trade corridors.
References:
-
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/23311983.2025.2495475#d1e192
-
https://intueriglobal.com/the-red-sea-crisis-in-global-trade/
-
https://www.wilsoncenter.org/article/timeline-houthi-attacks
-
https://www.ship-technology.com/features/houthi-attacks-in-the-red-sea-a-timeline-since-october/
-
https://www.worldbank.org/en/data/interactive/2025/04/08/global-supply-chain-stress-index
-
https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/effects-global-supply-chain-from-red-sea-crisis/
Tags:
What's your view?
About the Authors
Shreya is a Delivery Manager in Acuity Knowledge Partners supporting consulting & corporate clients, across sectors. She has over 11 years of experience in working with global clients, being single point of contact (SPOC) on a variety of engagements for business consulting, corporate strategy, and deal advisory, across multiple verticals.
She specializes in market research, strategy development, commercial & financial due diligence, benchmarking (operational, financial, technology, pricing, among others), go-to-market strategy, competitive intelligence, market/opportunity assessment, among other related services. Her responsibilities cover client handling/management, project management, team management, sales enablement, and quality assurance.
She also attended several technology oriented international conferences including Cloud Expo Asia, RSA Conference, DevOps India Summit,..Show More
Vandana Tokas is a senior associate in Acuity Knowledge Partners supporting consulting & corporate clients catering diverse sectors. She has over 6.5 years of experience in consulting and research support across sectors. She specializes in market research, strategy, and competitive analysis, and has delivered insights through industry studies, executive profiling, M&A research, and content creation. Her background also includes supporting fast-paced research requests across diverse industries, including benchmarking and internet-based analysis. She holds master’s degree in economics from IP university, Dwarka campus.
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox








