Introduction
Introduction
In today’s digital age, the importance of cybersecurity in finance cannot be overstated. As financial institutions rely increasingly on technology to process, store and transmit sensitive data, they become more vulnerable to cyberthreats. This article explores the future of cybersecurity and the possible threats to the financial sector.
“Cybersecurity refers to the technologies, processes and practices designed to protect networks, devices, programs and data from attack, damage or unauthorized access”, according to McKinsey & Company (15 March 2021). Cybercrime is a growing global threat that has significant economic and social consequences. It is estimated that cybercrime costs the global economy around USD600bn annually, equivalent to approximately 0.8% of the world’s GDP (source: CSIS, 2018).
Cybersecurity Threats
The importance of staying up to date with cybersecurity trends cannot be overstated in today’s technology-driven world. “Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, so it’s essential to keep up with the latest trends and techniques”, according to IBM (2021). In fact, Zhou, M and Ye, J (2020) argue that “cybersecurity trends are important because they help organizations anticipate and prepare for potential cybersecurity threats.” By understanding the latest cybersecurity trends for financial institutions, organisations can implement proactive measures to mitigate risks and protect their sensitive data.
There are three major threats the cybersecurity financial industry is focusing on, according to Zhou, M and Ye, J (2020): phishing attacks, IoT ransomware and cyberattacks on mobile devices.
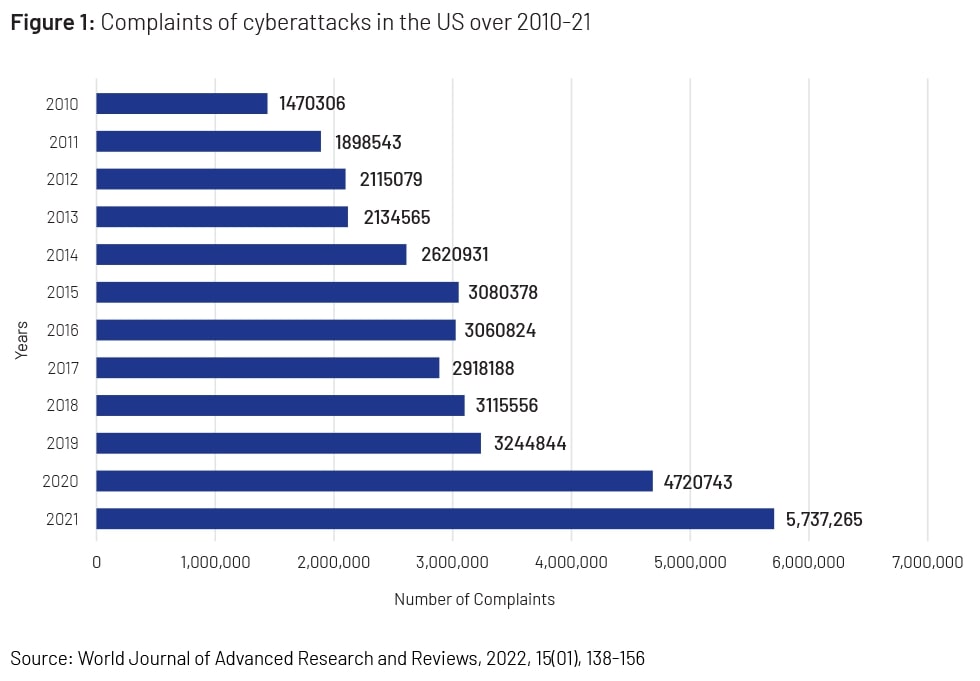
Complaints of cyberattacks grew 290.21% in the 12 years from 2010 to 2021 (Figure 1). Hackers are getting smarter, cybercrime prevention is expensive, everything is automated, vulnerabilities are everywhere and companies’ processes have become automated; more of their infrastructure is rooted in technology, according to Al-Omari et al (2022)
Cybersecurity Measures
These refer to the strategies and techniques used to protect computer systems, networks and data from unauthorised access, theft, damage or disruption. They include the following:
» Access control: This is used to regulate and limit access to data, based on predefined access, limiting access to sensitive data and systems to authorised personnel through the use of authentication mechanisms such as passwords, biometrics and two-factor authentication (source: Esposito, C, De Santis, A, Tortora, G, Chang, H and Choo, K K R, 2018).
» Encryption: This refers to encoding sensitive data so it cannot be read by unauthorised individuals even if it is intercepted. Encryption uses cybersecurity for financial institutions to defend against brute force and cyberattacks, including malware and ransomware (source: IBM, n.d.).
» Firewall: This is a network security device that scrutinises incoming and outgoing network traffic and decides whether to authorise or prohibit specific traffic based on a predetermined set of security rules (source: Cisco, n.d.).
» Antivirus software: This is a program designed to detect and remove malicious software such as viruses, worms and Trojan horses (source: CISA, 2021).
» Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS): An IDS is designed to observe network traffic, scrutinise it for recognisable attack patterns and notify administrators if any suspicious activity is detected while allowing traffic to continue uninterrupted. An IPS, like an IDS, also examines network traffic but is capable of taking action to prevent the identified threats (source: Okta, n.d.)
Encryption Algorithms
Encryption algorithms are classified into two groups: symmetric-key (also called secret-key) and asymmetric-key (also called public-key) encryption. Symmetric encryption is also called conventional encryption, as it uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. On the other hand, asymmetric encryption uses different keys for encryption and decryption.
Asymmetric encryption techniques are approximately 1,000 times slower than symmetric encryption techniques, according to Singh, G (2013). This makes it unfeasible to encrypt large amounts of data. Additionally, to achieve an equivalent level of security as afforded by symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption requires a stronger key.
Learn more about quantum computers and cybersecurity. Download the document now.




