Published on July 10, 2025 by Pooja Khandelwal
ESG investing in private markets integrates environmental, social and governance (ESG) attributes into the investment mechanism.
ESG investing through the ages
ESG investing has its roots in 18th century ethical finance, which was shaped by thinkers including John Wesley and Adam Smith, who warned about the dangers related to environmental damage. The movement gained traction in 1928, when the US Pioneer Fund introduced the concept of socially responsible investing, avoiding investing in industries such as alcohol and tobacco.
By the 1990s, ESG investing began to formalise with the creation of the Domini 400 index, among others, and the rise of the ‘triple bottom line’ concept. During this era, various ESG initiatives, such as the Principle of Responsible Investment (PRI) and the UN’s Who Cares Wines Report, were launched, emphasising the incorporation of ESG issues into investment.
By the 2010s, ESG became mainstream, fuelled by the Paris Agreement and the growing demand for sustainable investments. Today, it has become a powerful force even though it is facing challenges such as greenwashing and the need for standardisation.
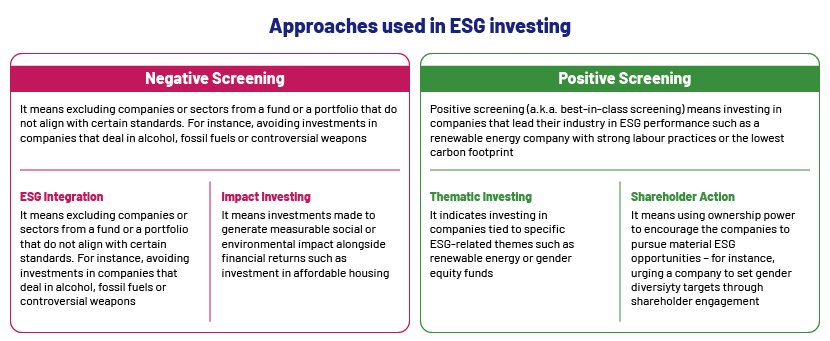
Source: Carbon Collective, Sustvest, Harvard Business School
Benefits of ESG investing in private equity
ESG investing has gained increasing prominence in private equity amid growing concerns around climate change, social responsibility and corporate ethics. Investors are prioritising both financial performance and long-term positive impact. Key benefits ESG investing brings to private equity firms include the following:
-
Improved risk management: By investing in companies that prioritise clean energy, responsible resources and strong governance, private equity firms can mitigate the hidden risks associated with environmental regulations, social unrest, and poor corporate governance. This approach will likely help investors avoid companies with risky or unsustainable practices. To reduce risks, many are using exclusionary screening to filter out problematic investments.
For example, a US-based medium-sized asset management firm used ESG screening during due diligence for potential investments. It found that a company had earned revenue from materials used in cluster bombs or nuclear weapons. Since the investee company was not able to clarify how its products were used, the asset manager decided not to invest.
-
Positive environmental impact: With increasing awareness and demand for sustainable practices, ESG investing has become a powerful tool for combating climate change, environmental degradation and social inequality. Thus, by investing in ESG-conscious companies, private equity firms can reduce carbon emissions, improve resource efficiency and promote clean energy solutions.
According to S&P Global, in 2023, private equity and venture capital firms invested USD4.6bn in renewable electricity – by continent, Europe led the way with USD9.2bn investment, while the US and Canada together contributed USD3.5bn .
-
Innovation and adaptability: ESG investing helps private equity firms stay flexible and forward-thinking. It encourages them to respond quickly to changing consumer preferences, market demands and regulations. Through AI, firms can analyse ESG data, predict risks and efficiently identify opportunities that support long-term growth and sustainability.
A US-based large asset management firm has integrated artificial intelligence into its investment processes through its in-house innovation unit. By analysing large data sets, market trends and company-performance metrics, AI helps identify patterns and unearths insights that may not be evident to human analysts, enabling more informed investment decisions and risk assessments.
-
Regulatory compliance: By focusing on environmental practices, employee welfare and leadership solidity, ESG investing helps private equity firms remain updated on growing global ESG regulations (including SFDR, SEC Climate disclosures and CSRD), which helps them avoid legal risks and keeps them well positioned in the market.
A Europe-based medium-sized to large asset management firm has conducted annual ESG assessments of its investment managers, covering areas such as ESG commitment, ESG integration into processes and transparent reporting. This structured approach ensures regulatory compliance and aligns with global standards.
Challenges in ESG investing in private equity
ESG investing offers promising opportunities to investors to invest in sustainability initiatives, but it is also exposed to challenges. To make informed and responsible investment choices, it is imperative that one understands the challenges:
-
Lack of standardisation: Currently, ESG information is scattered, inconsistent and lacks a standardised reporting framework. Thus, different rating agencies use diverse methodologies, making it difficult to compare companies on ESG outcomes.
-
Limited disclosures: Different companies make ESG disclosures to various degrees. Incomplete disclosure makes it difficult for private equity investors to gain a proper understanding of a company’s ESG practices. To overcome this shortcoming, private equity firms can collaborate with industry bodies and develop ESG initiatives.
-
Inability to validate data: Currently, there is no official system or governing body for verifying the ESG data reported by companies. This opens the door to potential greenwashing. To mitigate greenwashing, third parties should be employed to verify information to enhance the transparency and trustworthiness of ESG reporting.
-
Financial returns-impact imbalance: Finding the right balance between financial returns and measurable impact is a key challenge in ESG investing for private equity firms. Integrating ESG considerations may require trade-offs, making it harder for these firms to address financial returns and ESG objectives adequately.
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can help
Acuity offers in-depth research, ESG data analysis and compliance support to help incorporate sustainability into investment strategies. Our services include providing guidance on regulatory frameworks (such as PRI, TCFD and SFDR), thereby ensuring alignment with global standards. In addition, we offer hands-on support for preparing ESG disclosures and reports, enabling firms to enhance transparency and meet stakeholder expectations more effectively.
Sources
-
https://www.deutschewealth.com/en/our-capabilities/esg/what-is-esg-investing-wealth-management.html
-
https://blog.sustvest.com/types-of-esg-strategy-for-investing/
-
https://www.carboncollective.co/sustainable-investing/esg-investing
-
https://www.uspec.org/blog/from-risk-to-reward-how-esg-investing-is-revolutionizing-private-equity
-
https://www.tcs.com/what-we-do/industries/capital-markets/solution/esg-investing-data-challenges
-
https://www.ivp.in/resources/blogs/data-challenges-behind-esg-investing/
-
http://decimalpointanalytics.com/articles/solving-challenges-in-esg-investing
-
https://www.ft.com/content/dd1d2e7d-7c7c-4968-a3bb-c330965bf18f
Tags:
What's your view?
About the Author
Pooja Khandelwal is a Senior Associate at Acuity Knowledge Partners with over 6 years of experience in ESG assessments, reporting, and data analysis. She specializes in delivering customized ESG and sustainability solutions to clients across global markets. She holds an MBA degree in finance and HR from Banasthali Vidyapith.
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox








